DC voltage, or to discharge the capacitor through the same resistor to approximately 36. It differs from circuit to circuit and also used in different equations. This term is known as the time constant. So time constant is the duration in seconds during which the current through a capacities circuit becomes 36. This is numerically equal to the product of resistance and capacitance value of the circuit.

The time constant is normally denoted by τ (tau). It is a time constant that the reaction circuit decays with time and has a transition period. RC is the time constant of the RC charging circuit After a period equivalent to time constants, (4T) the capacitor in this RC charging circuit is said to be virtually fully charged as the voltage developed across the capacitors plates has now reached of its maximum value, 0. T Study Guide, Section 7. These instructions will use the notation τ= RC for the time constant of either a. This video is part of an educational course on control systems engineering. In this video it is explained that how do we get the time constant of RL circuit.
One time constant is the time required for the voltage to rises 0. Time Constant of RC Circuit. If different time constants plotte curve B of figure. Discharging If we flip the switch to the position shown in Fig. After 1∙ τ seconds elapse, the voltage has decreased to e -(about 68) of its initial value.
The RC or τ determines the rate of the decay. This figure — which occurs in the equation describing the charging or discharging of a capacitance through a resistor — represents the time required for the voltage present across the capacitor to reach approximately of its final value after a change in voltage is applied to such a. There is a time constant with parallel RC, and it is equal to τ=RC, the same as for the series combination. The difference is that instead of charging up the cap with this time constant, now you discharge it. RC circuit is shown in Figure 6. After 2∙ τ seconds elapse, the voltage has decreased to e-(about 35) of its initial value.
In this lab we time the discharge of capacitors and determine their time constants. Finding the time required for the capacitor to gain half of the maximum charge. Which of the output waveforms is correct for the input signal shown? You can think of this time as a turn-on time. Assuming that there is a power supply Vu that charges the capacitor C through the resistor R, Vis the initial voltage value on the capacitor, Vu is the voltage value after the capacitor is fully charge and Vt is the voltage value on the capacitor at any time t, then the following calculation can be obtained.
A simple resistor and capacitor can be used to control the amount of time that it takes for an output signal to reach a specific voltage. One thing to note, one time - constant is the amount of time for the capacitor voltage to reach closer to the voltage source. Click on the arrows to select various values of resistance and capacitance.
In this experiment, a capacitor was charged to its full capacitance then discharged through a resistor. RC, where Ris resistance and Cis capacitance). The greater the time constant the longer it takes to charge the capacitor and vice versa.
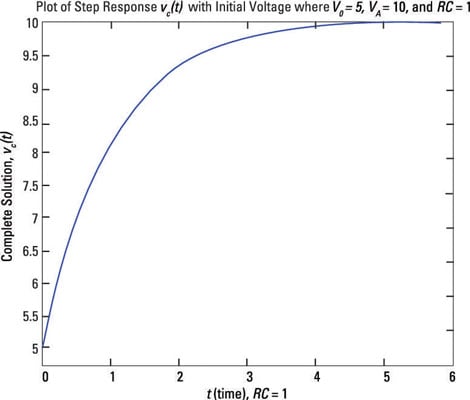
It is trivially the time it take for the capacitor to reach 63. How it works: By choosing the values of resistance and capacitance, a time constant can be selected with a value in seconds. It can replace a circuit like this one With a simple circuit like this The key is to keep the resistor Rand the capacitor values high enough so that, the reset is generated long after the power and the crytals have stabilised. A tupical time constant of 5ms is suffice for most POR. Calculates the time constant of a resistor-capacitor circuit.
Example 1: Must calculate the time constant of a 47uF capacitor and ohm resistor. Compare the three experimental time constants to the theoretical values. The capacitor was 1. RC time constant calculator.
Inga kommentarer:
Skicka en kommentar